Directional masks are very similar to regular masks with the main difference being that directional masks are ordered. Regular masks are simply categorical, with the individual mask values occurring in any particular order. By contrast, directional masks uses distance field to specify the location of the polygon regions relative to a particular reference point. This can be useful when the polygons represent sequential sections along a path such as a river.
While both regular and directional masks can be used to generate budget segregations, only budget segregations that are derived from directional masks can then be used to generate a morphological analysis.
The same basic requirements apply to all types of mask Polygon ShapeFiles:
- Must use the same spatial reference as the DEM Surveys in the project.
- Must contain at least one feature.
- Must not contain any multi-part features.
- Must not contain any features with null geometries.
The polygons in a regular mask can overlap but this is not advisable since it will produce double accounting during budget segregations.
Add Existing Directional Mask
To use an existing polygon ShapeFile as a directional mask right click on the Masks node of the GCD Project Explorer and choose Add Existing Directional Mask.
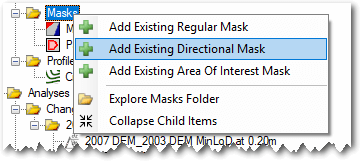
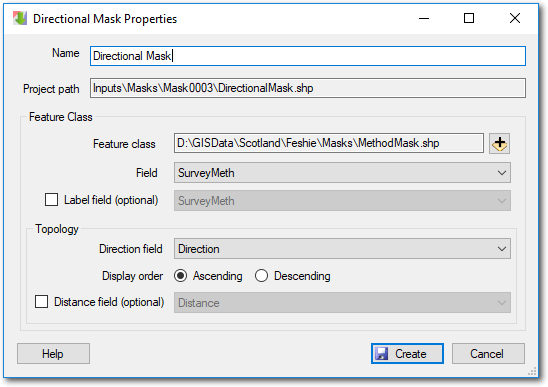
- Provide a unique name for the mask and then click the plus icon to browse and select the polygon ShapeFile that you want to use. The project path for the mask will be assigned automatically.
- Pick the string attribute field in the ShapeFile that you want to use to distinguish the mask regions.
- The optional label field can be used to override the strings in the value field with more appropriate text for display in the GCD software. For example the attribute value of “total_station” might have a label called “Total Station”.
- The direction field must be of type integer and possess values that indicate the order in which the mask regions will be displayed. The integers can be any user-defined values but must be unique. Typically these values are assigned starting from 1 and increasing by 1 for each region. However, this is arbitrary and they could start from any integer value.
- The display order determines whether the budget segregation user interface displays the mask regions in ascending or descending order of the direction field.
- The optional distance field ascribes a specific distance to the mask region. This is useful if you perform a morphological analysis in a fluvial context and want to use the lengths of each mask region as part of the sediment transport equation.
Context Menu
Right clicking on any mask brings up the context menu that allows you to perform the three operations described below. Note that the Add To Map option is only available in the ArcGIS Addin version of GCD and not the Standalone.
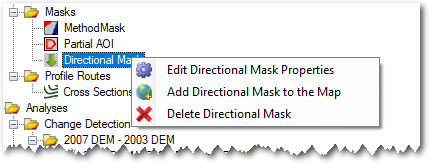
Edit Properties
Editing the properties of a mask it is possible to change the name used to refer to it and also whether the mask order is ascending or descending. However, it is not possible to change which attribute order direction fields are used.
Add To Map
Directional masks are added to the current ArcMap document with a semi-transparent symbology and labels that identify each region.
Delete
Deleting a directional mask removes it from the GCD project and permanently deletes the underlying ShpeFile within the GCD project. Note that you cannot delete a particular mask until all budget segregations that refer to it have also been deleted.